Difference between revisions of "MainPage:Nuclear:KaonDetector:Simulations:Codes"
Jump to navigation
Jump to search
| Line 16: | Line 16: | ||
{| border="0" halign="center" | {| border="0" halign="center" | ||
| − | |+'''First | + | |+'''First Kaon Aerogel Detector geometry for the simulations on GEMC''' |
|- | |- | ||
| valign="top"| | | valign="top"| | ||
| Line 27: | Line 27: | ||
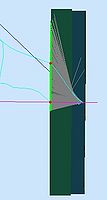
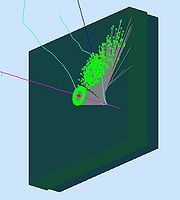
Setting the GEMC code to work with material optical properties, a high momentum Pion was generated to pass through the aerogel. The following pictures shows the first results on these simulation. The end plate was set to absorb the photons, so it was possible to see the cone of photons generated by the Cerenkov phenomena. | Setting the GEMC code to work with material optical properties, a high momentum Pion was generated to pass through the aerogel. The following pictures shows the first results on these simulation. The end plate was set to absorb the photons, so it was possible to see the cone of photons generated by the Cerenkov phenomena. | ||
| + | |||
| + | {| border="0" halign="center" | ||
| + | |+'''First Cerenkov radiation generated in Aerogel Detector, on GEMC simulation''' | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | | valign="top"| | ||
| + | [[File:1st_simulation_side.jpg|thumb|center|x200px|Side view of a <font color="magenta">Pion</font> passing though the detector, with velocity higher than the threshold of the Cerenkov phenomena. So a cone of <font color="dimgrey">photons</font> was created as a result of this phenomena.]] | ||
| + | | valign="top"| | ||
| + | [[File:1st_simulation_back.jpg|thumb|center|x200px|Back view of the detector. An electron was also created inside the detector, also generating <font color="dimgrey">photons</font> due to Cerenkov phenomena.]] | ||
| + | | valign="top"| | ||
| + | [[File:1st_simulation_3d.jpg|thumb|center|x200px|View of the back side of the detector. The photon absorption on the end plate is illustrated by <font color="green">points</font>.]] | ||
| + | |} | ||
Revision as of 23:56, 10 November 2011
| This page is under construction. It requires a review! |
| ⇐ Back to the Kaon Detector page |
First Simulations on GEMC
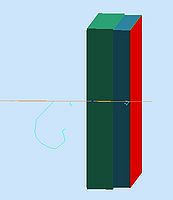
For the study of the Kaon Aerogel Cerenkov Detector in the SHMS, some simulations are being prepared using GEMC code. GEMC is a code based on the Geant4.
A first model of the detector was constructed using the standard library of the GEMC, with the standard materials and geometries. The following pictures show this first simplified model of the detector.
Setting the GEMC code to work with material optical properties, a high momentum Pion was generated to pass through the aerogel. The following pictures shows the first results on these simulation. The end plate was set to absorb the photons, so it was possible to see the cone of photons generated by the Cerenkov phenomena.