MainPage:Nuclear:KaonDetector
| ⇐ Back to the Main_Page |
Latest news
New aerogel tiles arrived for the Kaon Aerogel Detector! They have refractive index of 1.015... extremely fragile! See pictures on the Construction link bellow.
The pre-assembly of the Kaon Aerogel was done! Check status on the Construction link bellow.
Detector Construction and Characterization
| Detector Construction |
⇒ |  Pictures |
 Construction details |
 Reference Material | |
|
| |||||
| Components Characterization |
⇒ |  PMT |
 Aerogel |
 Reflective Materials |
 Sealant |
|
| |||||
| Experiments | ⇒ | x150px Full Detector tests |
x150px Prototype tests |
||
|
| |||||
| Simulations | ⇒ | x150px Full Detector simulations |
x150px Prototype simulations |
x150px Scripts and codes | |
Universities consortium for the construction of this new detector
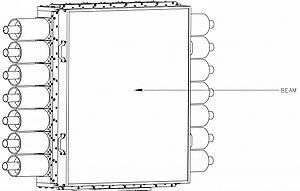
As part of the upgrades on the Hall C at JLab, a new Kaon Aerogel Detector is under construction by a collaboration of researchers on Particle Physics, lead by Dr. Tanja Horn.
The main purpose of this detector is to be part of the new spectrometer that is being constructed at Hall C, the SHMS.
For the execution of the project, a consortium was established with the following institutions:
- The Catholic University of America
- University of South Carolina
- Mississippi State University
- Florida International University
Two other partners are also engaged on this project, as unfunded institutions:
This project is founded through a NSF grant: PHY-1039446.
General Aspects on the Detector
The design of this detector is based on proven technology and benefits from many years of experience that JLab acquired on the usage of aerogel detectors.
The idea behind an aerogel detector is to make possible the triggering of events (particle) from a nuclear reaction for the selection of particles momentum. Together with other information on the experiment (e.g. beam energy and spectrometer angle), it makes possible the particle identification (PID) from a nuclear reaction.
The special characteristic of an aerogel detector for the PID is a threshold that happens with the Cerenkov radiation phenomenum. Only particles above a threshold velocity will produce this effect. The threshold is directly related to the refractive index of the aerogel inside the detector.
The detector that is under construction in this project will feature three trays of aerogel, each with a different refractive index. This design will provide the flexibility to change the threshold on the momentum selection of the particles, and thus cover the full kinematic range needed by the experiments. Aerogel material of two refractive indices is already at hand.