Difference between revisions of "MainPage:Nuclear:KaonDetector:AerogelCharacteristics"
| Line 13: | Line 13: | ||
In order to starting measuring the light absorption properties of aerogel, a spectrometer was used for the measurement of the transmittance of some tiles (figure 1). | In order to starting measuring the light absorption properties of aerogel, a spectrometer was used for the measurement of the transmittance of some tiles (figure 1). | ||
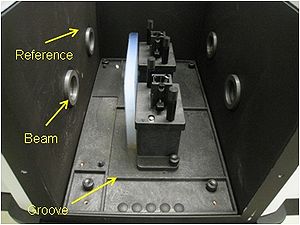
| − | The spectrometer consists of a | + | The spectrometer consists of a monochromatic beam of light (1 nm resolution) that is chopped in two different paths: reference and beam (figure 2). One aerogel tile is placed on the beam path (figure 3), so the spectrometer measures the light intensity difference between the beam and reference path, giving the transmittance of the analyzed sample. |
{| border="0" style="text-align:center;" width="100%" | {| border="0" style="text-align:center;" width="100%" | ||
| − | |+''' | + | |+'''Experimental setup for aerogel transmittance characterization''' |
|- | |- | ||
| valign="top"| | | valign="top"| | ||
| − | [[File: | + | [[File:Spectrometer_Perker750.jpg|thumb|center|300px|1) Equipment "Perkin/Elmer Lambda 750 Spectrometer" used for the analysis.]] |
| − | + | | valign="top"| | |
| + | [[File:Spectrometer_beams.jpg|thumb|center|300px|2) Inside the spectrometer where the monochromatic light beam is chopped in two: reference and beam. The sample to be analyzed is placed in the beam position.]] | ||
| + | | valign="top"| | ||
| + | [[File:Spectrometer_tile.png|thumb|center|300px|3) Aerogel tile placed in the beam position for transmittance analysis.]] | ||
== Refractive index measurement == | == Refractive index measurement == | ||
Revision as of 17:54, 26 January 2013
| This page is under construction. |
| ⇐ Back to the Kaon Detector page |
Optical properties - Transmittance
In order to starting measuring the light absorption properties of aerogel, a spectrometer was used for the measurement of the transmittance of some tiles (figure 1).
The spectrometer consists of a monochromatic beam of light (1 nm resolution) that is chopped in two different paths: reference and beam (figure 2). One aerogel tile is placed on the beam path (figure 3), so the spectrometer measures the light intensity difference between the beam and reference path, giving the transmittance of the analyzed sample.
|
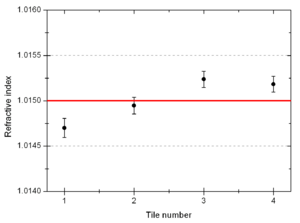
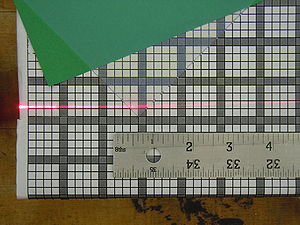
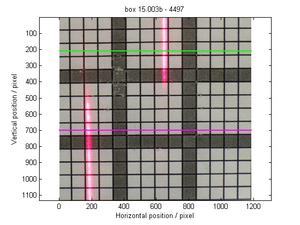
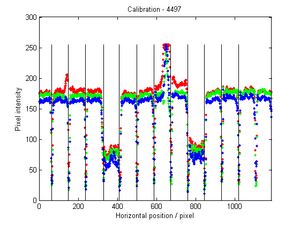
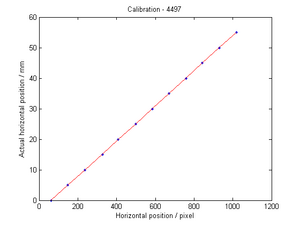
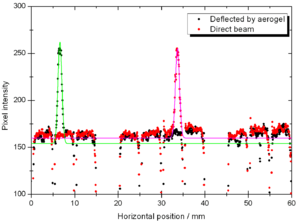
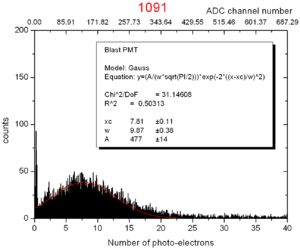
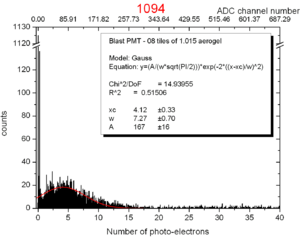
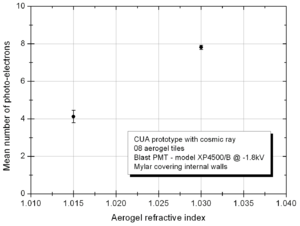
File:Spectrometer tile.png 3) Aerogel tile placed in the beam position for transmittance analysis. Refractive index measurementIn order to evaluate the quality of the aerogel tiles we bought for the Kaon Aerogel Detector, an experimental setup was prepared. Four tiles with refractive index 1.015 were randomly selected and analyzed. This method consists of a laser sheet, part of it passing through the analyzed aerogel tile and the other part passing out of it. The beam that goes inside the tile get refracted. A reference paper is placed after the tile to mark both the direct and refracted beams. The deviation of the laser is them possible to be measured (using image analysis) for the calculation of the refractive index that causes such deflection. Kaon Aerogel Detector prototype - Aerogel light yield comparisonIn order to compare the different aerogel (refractive index) we will use in the Kaon Aerogel Detector, a set of cosmic rays data was acquired with the CUA's prototype. Details of the prototype can be found in the Prototype page. To evaluate the relative light yield of the aerogel tiles with refractive indexes 1.030 and 1.015, the setup was run with the same configuration twice (just exchanging the aerogel). The setup configuration was kept as follows:
To see a similar test done for the analysis of the different PMTs options for the Kaon Aerogel Detector, click here. |